EUR/CHF: An Overview

The forex symbol EUR/CHF indicates how much the Euro (abbreviated as EUR) is worth in relation to the Swiss Franc (abbreviated as CHF), and how many Swiss Francs you need to buy one Euro. The pair is nicknamed “Euro-swissie” in the FX market.
As a cross-currency pair, EUR and CHF are traded directly, without the need to convert to a base currency first. This is also commonly known as currency pairs that do not involve the US Dollar (USD). The EUR/CHF currency pair is among the most popular cross-currencies in the forex market.
In this article we breakdown the history of these currencies, their dynamics, and how you can trade this pair.
For more currency pair breakdowns, check out our USD/JPY Overview.
Currency background
The Euro (EUR)
As of 2022, 19 out of the 27 member countries of the European Union (EU) use EUR as their official currency.
Since its debut in 1999 and entry into circulation in 2002, EUR has become one of the most widely used currencies for financial transactions worldwide, often second only (or at times at par with) USD.
Owing to its credibility, EUR has also, until recently, been a relatively stable currency. This stability has allowed it to extend its importance well beyond the EU. Over 50 other countries and territories globally have adopted the EUR as currency or have pegged their currencies to EUR. Furthermore, it accounts for over 20% of global foreign exchange reserves, second only to USD.
The Swiss Franc (CHF)
CHF is the official currency of Switzerland, as well as of Liechtenstein. In contrast to EUR, CHF traces its origin over a century back to 1850.
CHF is among the top ten most traded currencies globally. It has long been considered a safe-haven currency, owing to the stability of the Swiss economy and its political neutrality. However, unlike EUR, no other country uses CHF as a peg for their own currency.
What to consider in trading EUR/CHF
Compared to most currency pairs in the market, EUR/CHF experiences fewer price movements. The trends are typically slower and more stable.
Several factors affect the prices of currency pairs in the forex market. For most currency pairs, price movements are mostly tied to economic and geopolitical circumstances, both locally and globally.
Here are some factors that drive EUR/CHF movements:
Economy
The EU, as a single market, is one of the largest economies in the world and one of the three most prominent players in global trade. It is Switzerland’s primary trading partner, with the EU accounting for over 60% of Swiss imports and receiving over 40% of Swiss exports. The economic situation in the Eurozone has a history of affecting the Swiss economy, such as in the 2010s.
If you’re trading EUR-based pairs, you can keep up to date with happenings in the EU economy through European Commission economic reports, including economic forecasts and reviews, as well as Fusion's Economic Calendar. The European Central Bank also publishes economic bulletins that provide insights on monetary policy, a key determinant of currency strength.
Swiss policies
The Swiss National Bank, which issues CHF, has traditionally been non-interventionist. Several of its moves, however, have impacted currency markets. In 2011, it pegged the CHF to EUR, in a move to help Swiss businesses to increase their profitability. A few years later, in 2015, it abandoned the peg, stunning investors, causing market turmoil, and leaving a profound impact on the EUR.
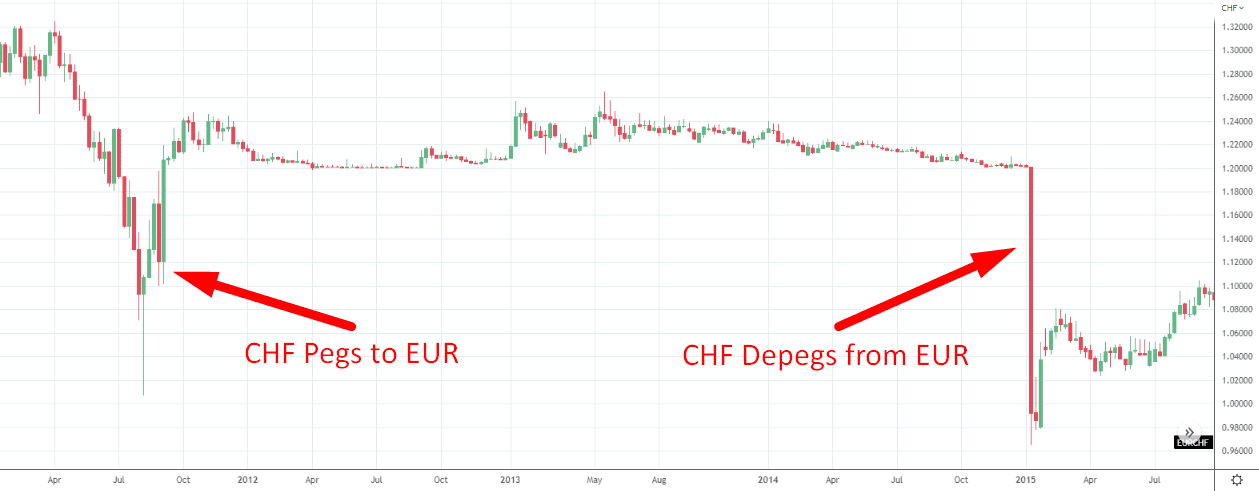
EUR/CHF 2011-2015 Weekly Time Frame
Global risks
Investors on the move to mitigate global economic risks are drawn to CHF due to its solid reputation for financial stability. In the aftermath of the global financial crisis in the late 2000s, widespread buying of CHF saw a 20% depreciation of EUR to CHF.
Geopolitical conditions
Investors also turn to CHF in times of political uncertainty in the EU, such as during the Greek sovereign debt crisis following the 2008 financial crisis. Demand for CHF had also soared during the Brexit negotiations, with investors using it as a hedge for protection against Brexit.
Movements in USD
A distinct advantage of EUR/CHF is its independence from USD. As they can be directly traded with each other, the pair isolates traders from USD-related volatilities.
Conclusion
The EU is one of the largest economies in the world, with EUR used in a majority of global transactions. The EU and Switzerland are not only geographically close, but also share strong economic ties, such as trade relations.
The EUR/CHF as a cross-currency pair experiences fewer price movements, with less volatile trends compared to other forex pairs. Both currencies are credible, with CHF long considered a safe-haven currency. Even during the COVID-19 global pandemic, investors have trusted CHF.
If you're looking to trade EUR/CHF, you'll be able to get ultra-tight spreads and $2.25 commissions per lot with Fusion Markets. Don't wait on the sidelines, be part of the action.
We’ll never share your email with third-parties. Opt-out anytime.